Tubular Breasts:
What is a tubular breast?
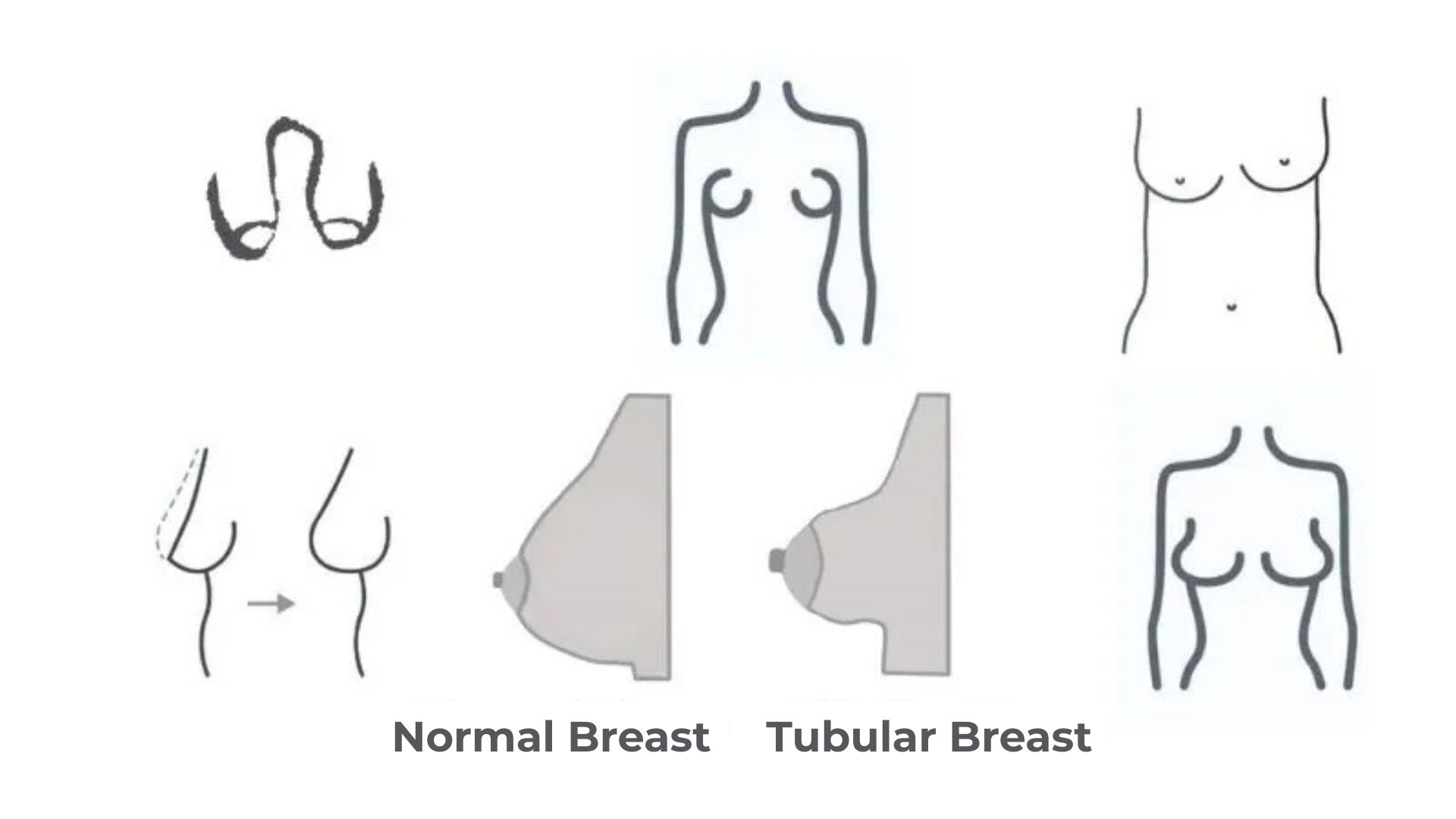
Tubular breast is a condition where the breast has an abnormal shape, which is caused by the developmental issues occurring during puberty. The condition resulted in a narrow, long appearance in the breasts, which lack a highly developed areola and normal breast tissue.

The key features of tubular breasts are included:
- Narrow, conical shapes: Breasts often appear small, elongated, and misshapen.
- Large, Puffy Arole: Erolus is generally wider and puffier and can protrude.
- Asymmetry: One breast may be different in size compared to another.
- Underdeveloped lower part of the breast: The lower half may lack perfection in the lower half, making the breasts look less round.
This condition can affect both small and large breasts, although it is often more noticeable in women with small breasts.
Treatment options for tubular breasts usually include breast enlargement surgery or breast lift to correct size and volume, restoring a more natural, symmetrical form.
What do tubular breasts look like?
Tubular breast appearance: long, narrow, cylindrical. The tuberous breast has a hollow appearance. The lower part of the breast is underdeveloped. The nipples may appear herniated.
What are the symptoms of tubular breast?
Tubular breasts may appear in the following forms:
- Cylindrical breast appearance,
- The large areola (the coloured, ring-shaped area around the nipple),
- Herniated areola,
- Asymmetry between the two breasts,
- Volumeless, deflated, elongated breast tissue,
- Proximity of the nipple to the inframammary fold,
- Breasts positioned far apart from each other,
- Absence of breast base or underlying breast tissue.
What causes tubular breasts?
Although the exact cause of tubular breasts is unknown, genetic factors are thought to play a role.
Underdeveloped breast tissue during the foetal stage or deformation of the breast tissue during puberty may cause tubular breasts.
How can I examine my breasts at home?
The simplest way to check for tuberous breasts at home is to bend forward in front of a mirror and examine the shape of your breasts. If the base of the breast appears narrow, long, drooping, flat (lacking volume) and cylindrical, you may have tuberous breasts.
How to fix tubular breasts naturally?
Tubular breasts do not resolve on their own. There may be a decrease in breast tissue sufficient to inhibit milk production. However, even if the condition is not that serious, the individual may feel self-conscious and experience psychological distress. Those wishing to remedy this appearance may consult a plastic surgeon to learn about breast aesthetic surgery.
Tuberous Breast Correction
Tubular breast treatment is possible through surgery. Different surgical techniques may be used depending on your complaints. These include breast augmentation, areola aesthetics, correction of nipple herniation, breast lift surgery, etc.

What is the treatment for tubular breast?
The treatment for tubular breasts is breast aesthetic surgery performed by plastic surgeon.
What is the surgery for tubular breast?
Tubular breast corrections involve surgical procedures. Treatment is planned individually for each patient. The techniques used in surgery are selected specifically for the patient. The following aspects are considered during planning:
- The percentage of missing breast tissue,
- Nipple aesthetics and nipple repositioning,
- Replanning the lower breast area,
- Breast lift,
- Correction of asymmetry between breasts, if present,
- Restoring the breast's natural oval shape,
- Breast augmentation,
- Breast implant placement.
Treatment Options for Tubular Breasts
Different tubular breast treatments are performed depending on the individual's complaint and breast structure abnormalities. These can be listed as follows:
Breast lift (Mastopexy):
Sagging breast tissue is lifted. Mastopexy achieves an aesthetic breast appearance.
Breast augmentation:
This is performed on individuals with small, narrow breast tissue lacking volume. It gives the breast a natural, aesthetically pleasing volume and size. The implants used can be placed under or over the muscle. Patient satisfaction rates after silicone breast surgery are quite high.
Reduction of the breast areola:
This procedure reduces the diameter of the overly enlarged nipple ring in tubular breasts to between 3.5 and 4.5 cm.
Correction of herniation in the breast areola:
The appearance of the herniated areola is corrected.
Widening of the breast base:
The structure of the narrow breast base is widened. It is made oval and fuller.
Fat injection:
Fat is injected into the breast. It is one of the methods that can be used to correct volume loss in the breast.
Recovery after tuberous breast surgery
Tubular breast surgery takes about 1-2 hours. Unless there are unexpected complications, the patient can be discharged on the same day.
Mild swelling, bruising, and pain may occur in the first few days. This pain can be relieved with prescribed painkillers.
Special bras worn by the patient after surgery support symmetrical healing. In this regard, it is critical to use the bras for the recommended period of time.
After surgery, the patient should not raise their arms too high or carry heavy weights.
Rest is recommended for the first week. A few weeks later, the patient can return to their daily life with the doctor's approval.
After 2 weeks, light exercise, such as walking, can be done
In the first month, the pain, swelling, and bruising will have largely subsided. It is important that the individual does not engage in strenuous exercise or lift heavy weights during the first month of healing.
Between the first 3 and 6 months, the shape of the breast begins to become more defined, and the breast softens. The colour of the stitches applied around the areola begins to fade.
One year after tubular breast surgery, the breast tissue takes its final shape. The surgical scars become so faint that they are no longer visible.
Where are the incisions made for tubular breast surgery?
Depending on the procedures to be performed, the surgical incision is generally made along the outer edge of the areola. This incision is usually sufficient for the operation. If different techniques are to be used for the operation, a straight incision is made at the base of the areola, reaching the inframammary fold.
In cases where breast implants are to be inserted, incisions may be made at different points depending on the technique used by your surgeon.
Does tubular breast surgery leave scars?
Minimal scarring remains from incisions made around the areola. Over time, the visibility of this scar diminishes. Scars from incisions made elsewhere are similar to those from other surgeries. Over time, their visibility diminishes and they do not cause an unsightly appearance.
Is there an age limit for tubular breast surgery?
The individual must have completed puberty for tubular breast (tube breast) surgery. Abnormal changes in breast tissue may be observed during puberty. Changes in breast tissue are completed around the age of 18-20. It is appropriate to wait until the age of 20 for tubular breast surgery.
Tubular breasts breastfeeding
If the tissue loss in the breast is severe enough to prevent breastfeeding, problems may arise during the breastfeeding period. If the tissue has developed sufficiently for breastfeeding, there will be no functional loss.
Tubular breasts may cause discomfort to the mother due to aesthetic concerns. If you are having a comfortable breastfeeding period and there is no functional impairment in your breasts, you can consult an aesthetic and plastic surgery specialist about your tubular breast concerns after the breastfeeding period.
Please contact us for more information.

